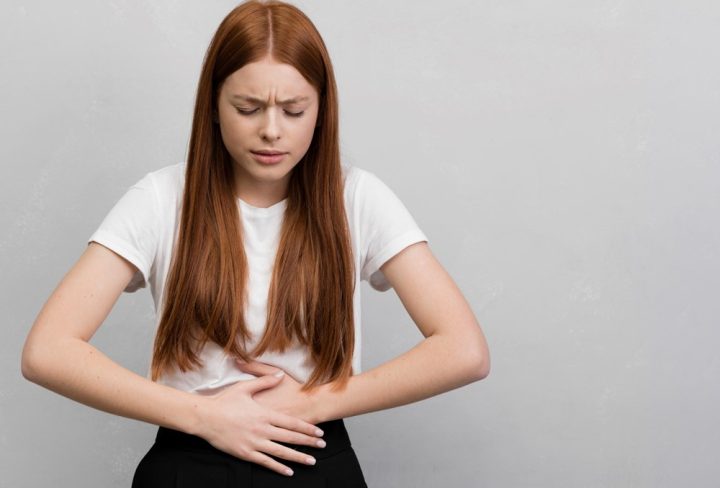
Peptic Ulcer Disease (PUD) is a chronic condition that affects millions of people around the world. It is characterized by the formation of ulcers in the lining of the stomach, esophagus, or duodenum. In this blog, we will explore the symptoms, causes, and treatment options for peptic ulcer disease.
Symptoms:
- Burning or gnawing pain in the stomach
- Feeling full or bloated
- Nausea or vomiting
- Loss of appetite
- Weight loss
- Dark, tarry stools or blood in vomit
Causes:
- Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infection: This is the most common cause of peptic ulcer disease, and it is estimated that H. pylori infection affects more than half of the world’s population.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): These medications can irritate the lining of the stomach and increase the risk of developing peptic ulcers.
- Excessive alcohol consumption
- Smoking
- Stress
Treatment Options:
- Antibiotics: If H. pylori infection is identified, antibiotics are usually prescribed to eradicate the bacteria.
- Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs): These medications reduce the amount of acid produced by the stomach and allow the ulcers to heal.
- H2 receptor blockers: These medications block the production of acid in the stomach.
- Antacids: These medications neutralize stomach acid and provide quick relief for symptoms.
- Lifestyle changes: Avoiding alcohol and tobacco, reducing stress, and making dietary changes can help manage peptic ulcer disease.
In conclusion, peptic ulcer disease is a common condition that can cause significant discomfort and affect a person’s quality of life. It is important to identify the symptoms and seek medical attention promptly. With the right treatment and lifestyle changes, most people with peptic ulcer disease can manage their symptoms and improve their overall health.